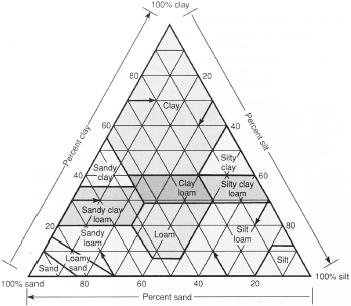
 Soil texture depends on the relative proportions of sand, silt and clay in a soil, as represented in this diagram. (McGraw-Hill Inc. Reproduced by permission.)
Soil texture depends on the relative proportions of sand, silt and clay in a soil, as represented in this diagram. (McGraw-Hill Inc. Reproduced by permission.)
The following sections of this BookRags Literature Study Guide is offprint from Gale's For Students Series: Presenting Analysis, Context, and Criticism on Commonly Studied Works: Introduction, Author Biography, Plot Summary, Characters, Themes, Style, Historical Context, Critical Overview, Criticism and Critical Essays, Media Adaptations, Topics for Further Study, Compare & Contrast, What Do I Read Next?, For Further Study, and Sources.
(c)1998-2002; (c)2002 by Gale. Gale is an imprint of The Gale Group, Inc., a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Gale and Design and Thomson Learning are trademarks used herein under license.
The following sections, if they exist, are offprint from Beacham's Encyclopedia of Popular Fiction: "Social Concerns", "Thematic Overview", "Techniques", "Literary Precedents", "Key Questions", "Related Titles", "Adaptations", "Related Web Sites". (c)1994-2005, by Walton Beacham.
The following sections, if they exist, are offprint from Beacham's Guide to Literature for Young Adults: "About the Author", "Overview", "Setting", "Literary Qualities", "Social Sensitivity", "Topics for Discussion", "Ideas for Reports and Papers". (c)1994-2005, by Walton Beacham.
All other sections in this Literature Study Guide are owned and copyrighted by BookRags, Inc.
The relative proportion of the mineral particles that make up a soil or the percent of sand, silt, and clay found in a soil. Texture is an important soil characteristic because it influences water infiltration, water storage, amount of aeration, ease of tilling the soil, ability to withstand a load, and soil fertility. Textural names are given to soil based on the percentage of sand, silt, and clay. For example, loam is a soil with equal proportions of sand, silt, and clay. It is best for growing most crops.
 Soil texture depends on the relative proportions of sand, silt and clay in a soil, as represented in this diagram. (McGraw-Hill Inc. Reproduced by permission.)
Soil texture depends on the relative proportions of sand, silt and clay in a soil, as represented in this diagram. (McGraw-Hill Inc. Reproduced by permission.)