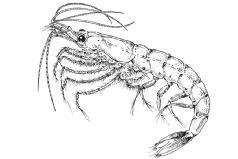
 Krill. (McGraw-Hill Inc. Reproduced by permission.)
Krill. (McGraw-Hill Inc. Reproduced by permission.)
The following sections of this BookRags Literature Study Guide is offprint from Gale's For Students Series: Presenting Analysis, Context, and Criticism on Commonly Studied Works: Introduction, Author Biography, Plot Summary, Characters, Themes, Style, Historical Context, Critical Overview, Criticism and Critical Essays, Media Adaptations, Topics for Further Study, Compare & Contrast, What Do I Read Next?, For Further Study, and Sources.
(c)1998-2002; (c)2002 by Gale. Gale is an imprint of The Gale Group, Inc., a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Gale and Design and Thomson Learning are trademarks used herein under license.
The following sections, if they exist, are offprint from Beacham's Encyclopedia of Popular Fiction: "Social Concerns", "Thematic Overview", "Techniques", "Literary Precedents", "Key Questions", "Related Titles", "Adaptations", "Related Web Sites". (c)1994-2005, by Walton Beacham.
The following sections, if they exist, are offprint from Beacham's Guide to Literature for Young Adults: "About the Author", "Overview", "Setting", "Literary Qualities", "Social Sensitivity", "Topics for Discussion", "Ideas for Reports and Papers". (c)1994-2005, by Walton Beacham.
All other sections in this Literature Study Guide are owned and copyrighted by BookRags, Inc.
 Krill. (McGraw-Hill Inc. Reproduced by permission.)
Krill. (McGraw-Hill Inc. Reproduced by permission.)
Marine crustaceans in the order Euphausiacea. Krill are zooplankton, and most feed on microalgae by filtering them from the water. In high latitudes, krill may account for a large proportion of the total zooplankton. Krill often occur in large swarms and in a few species these swarms may reach several hundred square meters in size with densities over 60,000 individuals per square meter. This swarming behavior makes them valuable food sources for many species of whales and seabirds. Humans have also begun to harvest krill for use as a dietary protein supplement.