 An electrostatic precipitator. (McGraw-Hill Inc. Reproduced by permission.)
An electrostatic precipitator. (McGraw-Hill Inc. Reproduced by permission.)
The following sections of this BookRags Literature Study Guide is offprint from Gale's For Students Series: Presenting Analysis, Context, and Criticism on Commonly Studied Works: Introduction, Author Biography, Plot Summary, Characters, Themes, Style, Historical Context, Critical Overview, Criticism and Critical Essays, Media Adaptations, Topics for Further Study, Compare & Contrast, What Do I Read Next?, For Further Study, and Sources.
(c)1998-2002; (c)2002 by Gale. Gale is an imprint of The Gale Group, Inc., a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Gale and Design and Thomson Learning are trademarks used herein under license.
The following sections, if they exist, are offprint from Beacham's Encyclopedia of Popular Fiction: "Social Concerns", "Thematic Overview", "Techniques", "Literary Precedents", "Key Questions", "Related Titles", "Adaptations", "Related Web Sites". (c)1994-2005, by Walton Beacham.
The following sections, if they exist, are offprint from Beacham's Guide to Literature for Young Adults: "About the Author", "Overview", "Setting", "Literary Qualities", "Social Sensitivity", "Topics for Discussion", "Ideas for Reports and Papers". (c)1994-2005, by Walton Beacham.
All other sections in this Literature Study Guide are owned and copyrighted by BookRags, Inc.
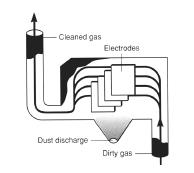
A technique for removing particulate pollutants from waste gases prior to their exhaustion to a stack. A system of thin wires and parallel metal plates are charged by a high-voltage direct current (DC) with the wires negatively charged and the plates positively charged. As waste gases containing fine particulate pollutants (i.e., smoke particles, fly ash, etc.) are passed through this system, electrical charges are transferred from the wire to the particulates in the gases. The charged particulates are then attracted to the plates within the device, where they are then shaken off the plates during short intervals when the DC current is interrupted. (Stack gases can be shunted to a second parallel device during this period). They fall to a collection bin below the plates. Under optimum conditions, electrostatic precipitation is 99% efficient in removing particulates from waste gases.
 An electrostatic precipitator. (McGraw-Hill Inc. Reproduced by permission.)
An electrostatic precipitator. (McGraw-Hill Inc. Reproduced by permission.)