 The sulfur cycle. (Illustration by Hans & Cassidy.)
The sulfur cycle. (Illustration by Hans & Cassidy.)
The following sections of this BookRags Literature Study Guide is offprint from Gale's For Students Series: Presenting Analysis, Context, and Criticism on Commonly Studied Works: Introduction, Author Biography, Plot Summary, Characters, Themes, Style, Historical Context, Critical Overview, Criticism and Critical Essays, Media Adaptations, Topics for Further Study, Compare & Contrast, What Do I Read Next?, For Further Study, and Sources.
(c)1998-2002; (c)2002 by Gale. Gale is an imprint of The Gale Group, Inc., a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Gale and Design and Thomson Learning are trademarks used herein under license.
The following sections, if they exist, are offprint from Beacham's Encyclopedia of Popular Fiction: "Social Concerns", "Thematic Overview", "Techniques", "Literary Precedents", "Key Questions", "Related Titles", "Adaptations", "Related Web Sites". (c)1994-2005, by Walton Beacham.
The following sections, if they exist, are offprint from Beacham's Guide to Literature for Young Adults: "About the Author", "Overview", "Setting", "Literary Qualities", "Social Sensitivity", "Topics for Discussion", "Ideas for Reports and Papers". (c)1994-2005, by Walton Beacham.
All other sections in this Literature Study Guide are owned and copyrighted by BookRags, Inc.
 The sulfur cycle. (Illustration by Hans & Cassidy.)
The sulfur cycle. (Illustration by Hans & Cassidy.)
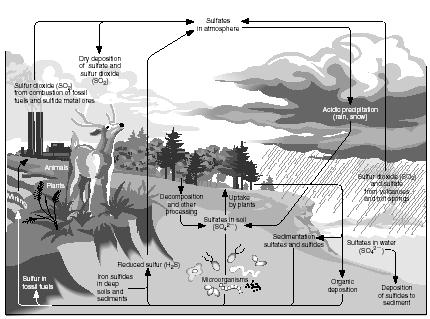
The series of chemical reactions by which sulfur moves through the earth's atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere, and biosphere. Sulfur enters the atmosphere naturally from volcanoes and hot springs and through the anaerobic decay of organisms. It exists in the atmosphere primarily as hydrogen sulfide and sulfur dioxide. After conversion to sulfates in the air, sulfur is carried to the earth's surface by precipitation. There it is incorporated into plants and animals who return sulfur to the earth's crust when they die. Through their use of fossil fuels, humans have a large effect on the sulfur cycle, approximately tripling the amount of the element returned to the atmosphere.